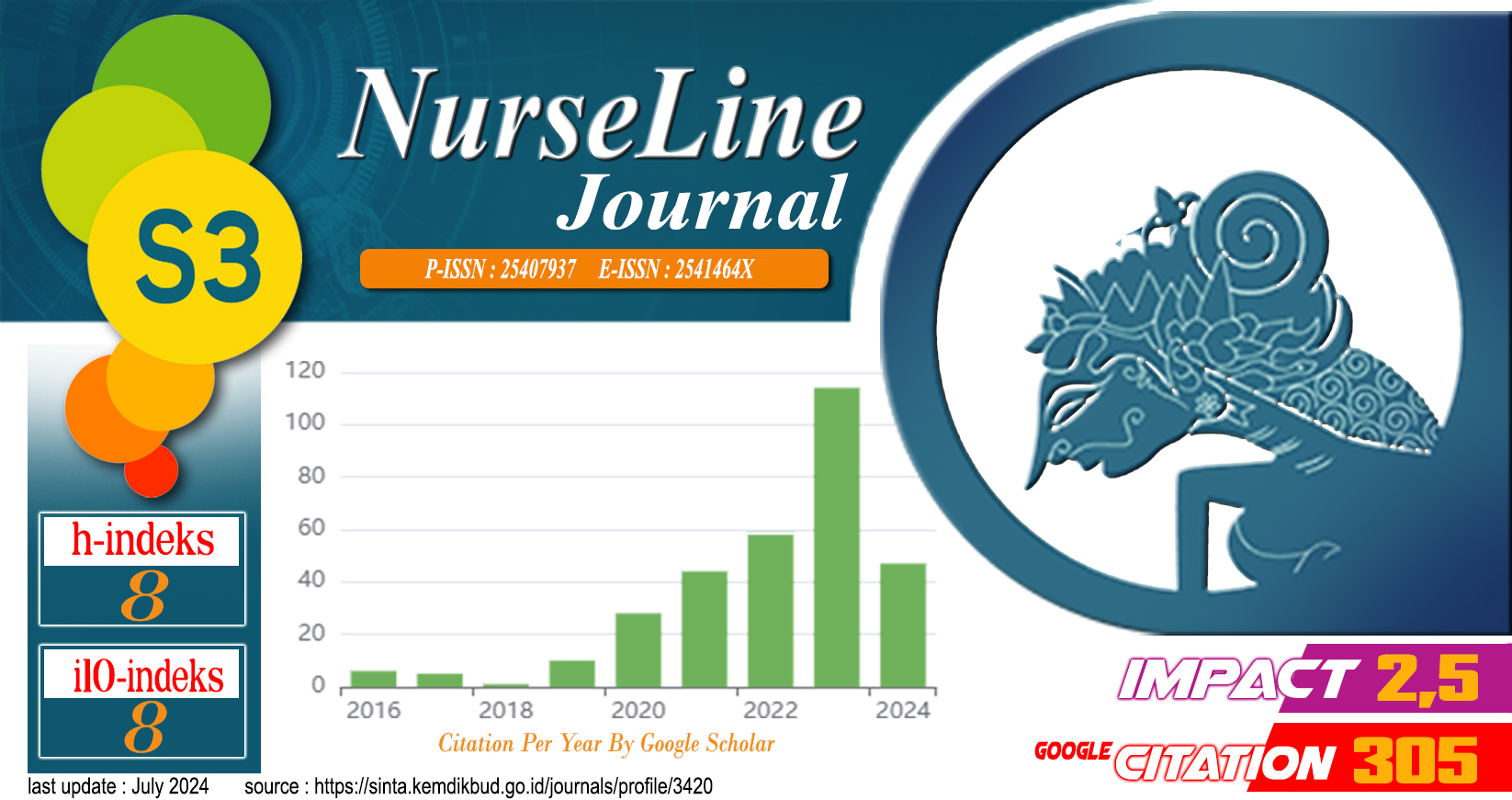
ASSESSMENT OF SUPPORTIVE CARE NEEDS IN PARENTS OF CHILDREN WITH THALASSEMIA
Abstract
Children with thalassemia must undergo a lifelong transfusion so that the family of children with thalassemia should be able to adapt to changes associated with the course of the disease in children with thalassemia. Changes that occur in the family of children with thalassemia include a change in supportive care needs that consist of practical, spiritual, psychosocial, information, emotional, and physical needs. This study aimed to identify the needs of supportive care in parents of children with thalassemia. This research was a quantitative descriptive research. A total of 32 respondents were obtained in this study by using accidental sampling within a period of 1 month. Data were collected using Supportive Care Needs Assessment Tool. Data were analyzed by applying descriptive statistical analysis. The results showed that the need of supportive care in parents of children with thalassemia from the highest that required assistance was the information needs (96.8%), emotional needs (81.25%), physical needs (78.13%), psychosocial needs (78.13%), spiritual needs (75%), and practical needs (65.13%). Based on the results of the study, it is recommended that health workers can design an intervention approach to help parents meet the needs of supportive care, especially the needs of information and emotional needs such as by giving information in general and specifically by forming supportive groups in parents.